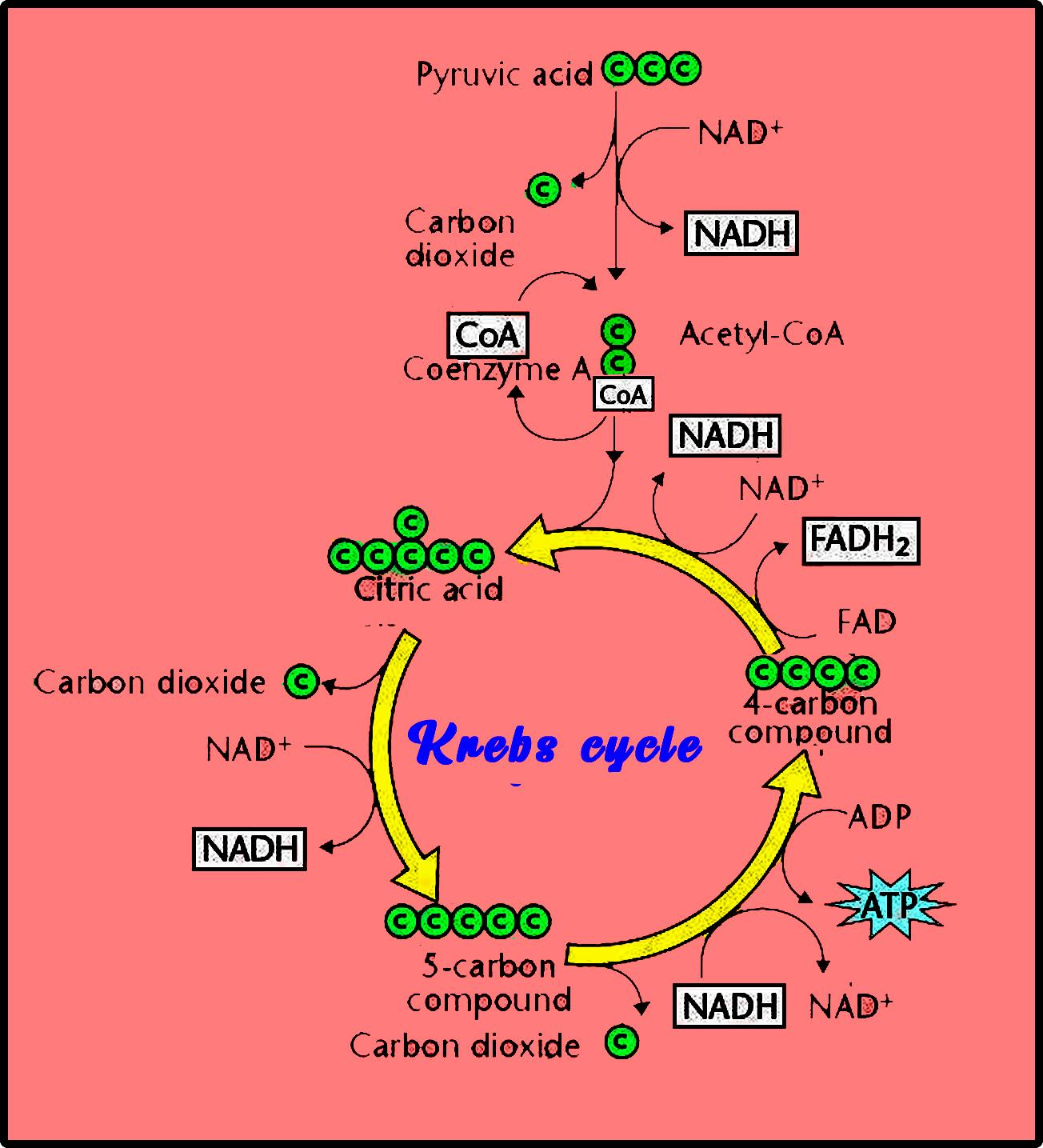
How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce . the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. Not only do plants produce sugars through. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that.
from exoamceay.blob.core.windows.net
explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. Not only do plants produce sugars through. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules.
How Much Atp Is Used In Krebs Cycle at Lynn Fiedler blog
How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. Not only do plants produce sugars through. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic.
From en.ppt-online.org
Cellular Respiration online presentation How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. Not only do plants produce sugars through. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Electron Transport Chain PowerPoint Presentation, free download How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From mungfali.com
Cellular Respiration Chart How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT “Cellular RESPIRATION” PowerPoint Presentation, free download How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Not only do plants produce sugars through. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water,. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From schematicfixfracture.z13.web.core.windows.net
Cellular Respiration Diagram Labeled With Atp How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. Not only do plants produce sugars through. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From enginedbpostulated.z22.web.core.windows.net
Cellular Respiration Diagram Labeled With Atp How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. the electron. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From cmagavern.weebly.com
Cell Respiration Biology How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Not only do plants produce sugars through. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. 1) is. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From sbi4u2015.weebly.com
Aerobic Cellular Respiration SBI4U How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. Although carbohydrates, fats and. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From exoamceay.blob.core.windows.net
How Much Atp Is Used In Krebs Cycle at Lynn Fiedler blog How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. the. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From biology.stackexchange.com
cellular respiration Why is ATP produced in photosynthesis used to How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. Not only do plants produce sugars through. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. the electron transport. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.slideshare.net
Cell Respiration (part 2) How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce Not only do plants produce sugars through. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.careerpower.in
Aerobic Respiration Definition, Equation and Examples How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. Not only. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.sciencefacts.net
Cellular Respiration in Plants Definition, Steps & Equation How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. This releases enough energy to. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From schematicempresssgdv.z22.web.core.windows.net
Energy Diagram For Cellular Respiration How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as reactants, aerobic. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. Not only do plants produce sugars through. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) +. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From www.researchgate.net
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production via the aerobic respiratory How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. with oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. Not only do plants produce sugars through. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) +. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From biologydictionary.net
[LS17] Cellular Respiration and Energy Biology Dictionary How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides, 6 molecules of water, and 32 molecules of atp. Although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are consumed as. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From quizgrouchiest.z4.web.core.windows.net
Cellular Nutrition And Respiration How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce the atp yield of plant respiration (atp/hexose unit respired) quantitatively links active heterotrophic. aerobic respiration requires oxygen (o 2) in order to create atp. Not only do plants produce sugars through. c6h12o6 (glucose) + o2 (oxygen) → 6co2 (carbondioxide) + 6h2o (water) + atp (energy) one molecule of glucose is oxidized to 6 molecules of carbon dioxides,. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.
From rileyzebsmall.blogspot.com
Final Electron Acceptor in Aerobic Respiration RileyzebSmall How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce Not only do plants produce sugars through. the electron transport chain (figure 13.4.1 13.4. explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 atp molecules. 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that. aerobic respiration. How Much Atp Does Plant Aerobic Respiration Produce.